Is it really possible to convert your car’s AC R12 system to R134a? Yes, it’s possible, and you’ll get to know how to convert it. It’s likely that the air conditioning system in the car you drive presently still uses R12 if it was manufactured before 1994.
Which means that the cars built after 1994 use R134a refrigerant. R134a must be used as a replacement for this refrigerant because it was identified as being environmentally hazardous.
Well, in this article, you’ll have a deeper understanding of the definition, differences, pros and cons, calculation, and how to convert your car’s AC R12 system to R134a. You’ll also know the frequently asked questions about converting the car’s AC R12 system to R134a.
What is the AC R12 system?
The AC R12 system is a common type of refrigerant used in air conditioners. We mentioned that cars that were built before 1994 use R12 refrigerant.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which are harmful to the ozone layer, make up R12. Due to this, the Montreal Protocol banned the production and use of R12 in 1987, but it took several years for the ban to be fully implemented.
What is the R134a system?
In many cooling and air conditioning applications, R134a refrigerant is commonly utilized. It was initially introduced to replace R12 in automobile air conditioning systems.
In coolers, it has also been used to replace the refrigerants R12 and R500. In both commercial and residential settings, it is utilized as a medium-temperature system.
Differences between the AC R12 and R134a systems
R134a’s molecules are smaller in size than those of R12, thus there was concern that it could leak through the hoses and flare fittings used in R12 systems. Compressor seals may leak in R134a systems because they run at higher discharge-side pressures than R12 systems.
The absence of CFCs in R134a makes it a lot different from R12 in comparison. Due to the fact that R134a is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC), it does not harm the ozone layer. HFCs still act as greenhouse gases and promote climate change.
The fact that R134a systems use less refrigerant than R12 systems is another major difference. This is due to R134a’s better cooling performance compared to R12.
Pros and cons of converting to R-134a
There are lots of advantages you’ll get from converting to the R134a system. The R134a refrigerant is safer to use based on the fact that the R12 refrigerant contains chlorofluorocarbons, which are harmful to the environment.
The R134a is also available for purchase, while the R12 is no longer available due to the fact that it has been banned for its harmful effects.
However, a major disadvantage of converting to R134a is the cost of the conversion. Depending on the tools used and the price of the refrigerant at the time, converting can cost anywhere between $100 and $300.
An unprofessional job could result in mistakes like overcharging the air conditioner, letting refrigerant escape, or causing a gas leak. To avoid these problems, however, you need to take your car to a professional, who might charge you at least $1,000.
How to calculate how much R134a is needed
Compared to R12, R134a refrigerant is lighter. You must charge the new system to between 75 and 85% of its factory-set capacity to ensure proper cooling. Using the specs for the current system, multiply the R12 charge by 0.9 or 90% to determine the refrigerant capacity.
From this number, subtract 1/4, or 0.25 pounds. R134a won’t provide the same level of cooling as R12, though. You might find that the system doesn’t get as cool even after properly charging it. R134a is still far more resistant to under- and overcharging.
How to Convert Your Car’s R12 System to R134a
There are specific conversion kits available that include all the required parts for the conversion for many different car models. Pressure switches need to be replaced on some models as well.
A proper conversion also requires the replacement of all the O-rings, a new accumulator, a new filter, and other components. If your car is old, however, it probably isn’t worth doing all of this since it will cost you more than $1500 and $2000.
On the other hand, it is not a long-lasting solution to simply change the fittings and add the right amount of R134a, even though this will work well on most older car models.
Completely discard the R12 from the system
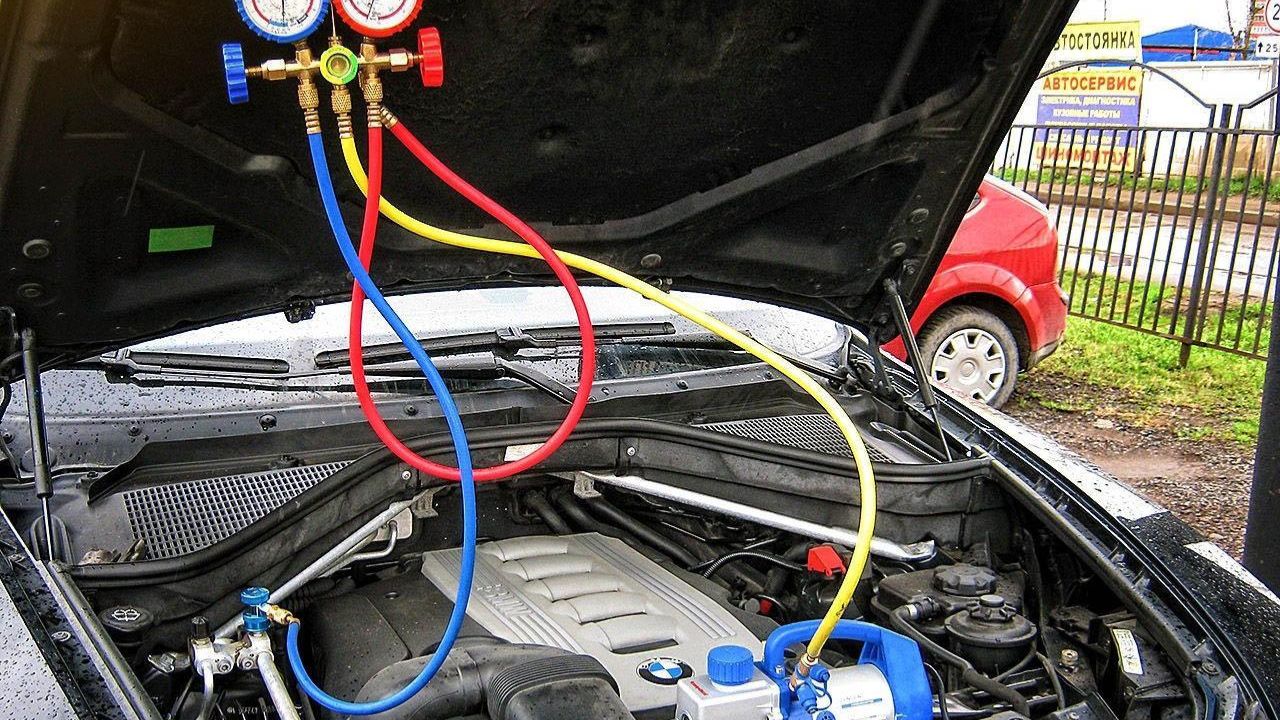
Connect the vacuum pump to the AC system’s low-pressure side. This is usually found near the evaporator. Pump out the R12 refrigerant that is currently in the system before you do anything else because it needs to be disposed of properly.
To collect the R12 refrigerant, connect the empty canister to the pump. Start the vacuum pump by opening the valve.
To completely discard R12 from the system, run the vacuum pump for about 50 minutes to an hour. The vacuum pump should be turned off and disconnected from the AC system when all of the R12 has been taken out.
Install an R134a adapter kit
Find the low-pressure side service port for the AC system. It is to this that the adapter kit will be attached. Clean any debris from the threads after removing the cap from the service port. The R134a adapter should be connected to the service port and snugged up.
Recharge the system with the right amount of R-134a.
The next step on how to convert AC R12 to R134a is to recharge the system with the R134a after installing the recharge kit.
To attach to the R134a can, use the yellow hose. There ought to be oil in this refrigerant already. If not, you’ll need to add that on your own. The can’s top valve should be turned. Start the car’s engine and turn on the air conditioner to its maximum setting.
To gauge the temperatures blowing out, you can insert a thermometer into the vent.
You should open up the system so that the refrigerant may be drawn from the can while the blue hose is attached to the low-side port.
The proper capacity, which is less than what was required with R12, can be reached by adding R134a until you reach it.